In television programs, database security breaches are often announced with klaxon-like buzzers and flashing lights. Any IT professional knows that, in real life, that is rarely the case.
Real-life data breaches don’t announce themselves. The average cybersecurity threat isn’t detected and contained until 277 days after the breach. You’ll need a proven process to identify and mitigate database security threats to avoid and detect breaches.
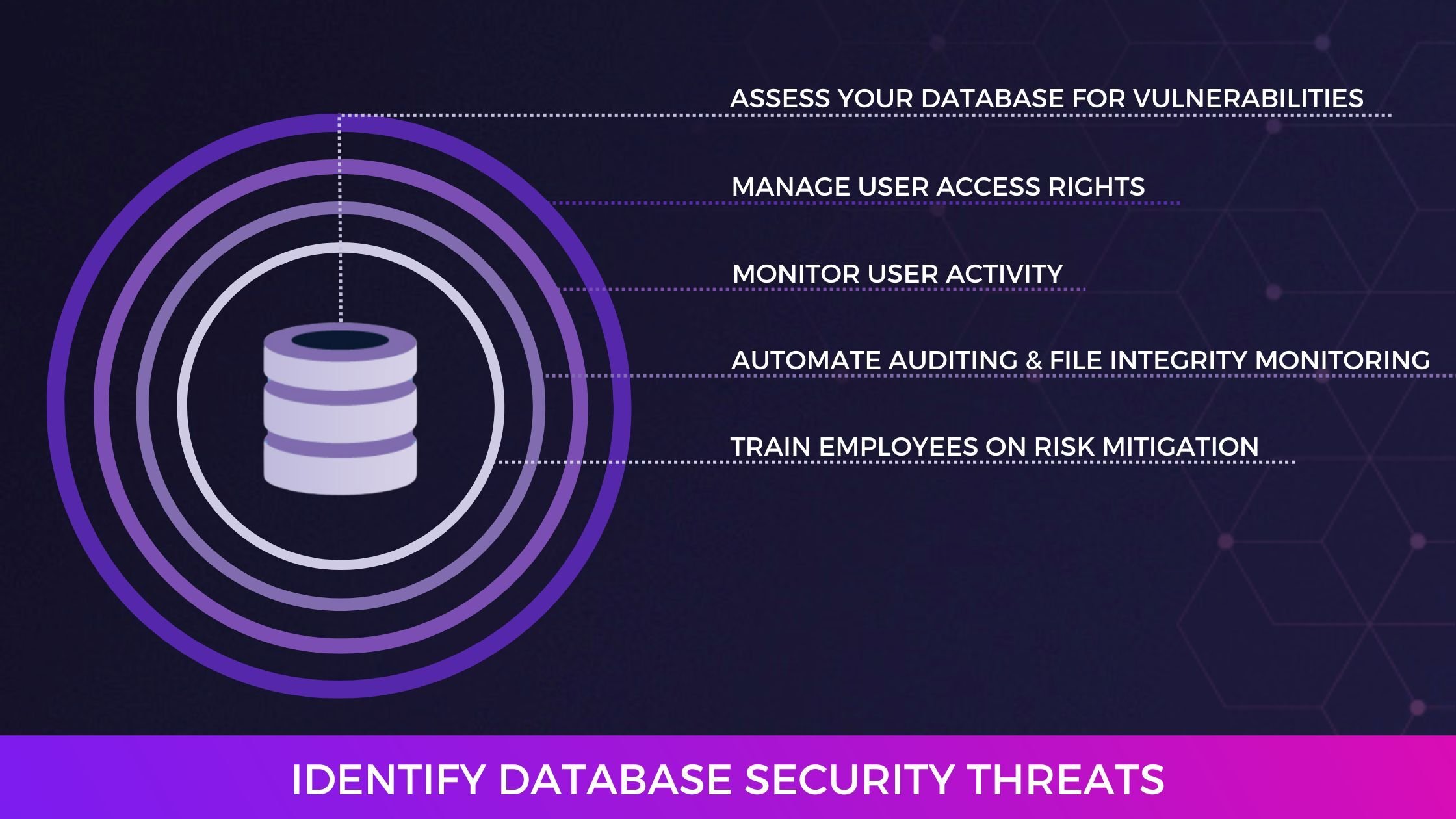
This post will provide a five-step process your team can follow to identify database security threats in your organization. After reading, you will have the tools you need to get started with database security improvements for your business.
Understanding Database Security Threats
Before we walk through the steps of how to identify database security threats, let’s discuss security threats in general. Simply put, a database security threat is anything that threatens your database’s confidentiality, availability, or integrity.
You need to be aware of common threats to your organization.
- SQL Injection: This threat occurs when malicious actors place code into web-based applications to access the backend database.
- Denial of Service: Denial of Service, or DoS, is a type of threat that slows down your server, resulting in a poor user experience.
- Poorly Managed Sensitive Data: If you don’t have sufficient practices to keep your organization’s data safe, you risk exposing your data to attacks.
- Weak Audit Trails: Similarly, insufficient practices to track database events can result in trouble when your organization is audited for data storage practices.
- Misconfigured Databases: If your database isn’t tailored to your business, you open yourself up to outside threats. Anything left to default settings is particularly vulnerable.
Protecting your organization from these threats is a significant concern. There are five steps businesses can take to help with database security.
1. Assess Your Database for Vulnerabilities
The first step is closely examining your database. During this step, you should check for possible vulnerabilities an attacker may target in the event of a breach.
Remember, all databases comprise three basic pieces: your data, configuration files, and metadata. Metadata and configuration files are often overlooked when considering database security. However, the only way to keep your database secure is to monitor the integrity of all three pieces.
Elements you want to pay special attention to during this step include:
- Critical assets: Note of assets you believe most likely to be targeted or most subject to compliance regulations.
- Redundancies: Watch for redundant features or data across multiple tools or systems.
- Known violations: If you know any current policies or practices that violate existing regulations, make a note of those here.
- Outdated systems: Examine your systems to see if any require patches or updates.
This step will prepare your organization for system hardening. You can achieve system hardening by taking control of your database in a manner that helps minimize attack vectors and compress your attack surface.
2. Manage User Access Rights
Step two of identifying database security threats is to examine your users’ access rights. Granting users excessive privileges within your database can significantly threaten your database security.
You increase the likelihood of internal threats when you provide users with more access than they need to do their jobs. Even if every member of your organization can be trusted, an external threat can do more damage in this scenario as they will be able to move laterally within the system once they have access.
The best solution to this challenge is to enforce the “least privilege” principle. Under this principle, you will grant users only the access they need to do their daily duties. Least privilege is one of the core tenets of Zero Trust, which is a database architecture you may want to consider exploring to increase security.
3. Monitor User Activity
The next logical step is to monitor user activity within your database. This practice will allow you to identify unusual activity that could indicate malicious intent, malware, or other threats.
You may also want to track users accessing or attempting to access unnecessary data for their daily job duties. Flagging any users accessing unusually large numbers of files or documents, even if they are related to their duties, can also be a sign of ransomware and is something to monitor.
Tracking users' unauthorized changes and the users who made the changes in your system is crucial at this stage. Having a robust and holistic view of what users are accessing within your database will give you the tools you need to identify a breach early on and take measures to solve it.
4. Automate Auditing and File Integrity Monitoring
You may have already realized this, but auditing and tracking user access is not a manual job. To effectively manage your database security processes, you need to automate wherever possible. This is often done with file integrity monitoring software.
Implementing a system integrity assurance solution can help you monitor database activity and identify threats and possible breaches. CimTrak is a file integrity monitoring tool with system integrity assurance that monitors all changes made in your target systems and applications, allowing for easy, reliable reporting and analysis.
CimTrak also helps you guard against unauthorized changes by offering immediate change reconciliation. Once CimTrak identifies an unauthorized change, the change can be automatically reversed to the system baseline.
5. Train Employees on Risk Mitigation
Your database security tools are critical, but you’ll fight an uphill battle without employee training. Even if you have the best security measures in place, you’re still susceptible to breaches, especially considering that 68% of data breach incidents occur due to human error.
To combat this challenge, conduct regular training with your employees. Some topics you will need to ensure you offer training surrounding include:
- How to recognize phishing attempts
- Password management best practices
- Safe internet usage
During these training sessions, ensure that you include any information relevant to your team, business, or industry.
Continuously Identify Database Security Threats
Identifying database security threats isn’t a process that can be done occasionally. To keep your data secure, you need to identify threats as soon as they arise.
Implementing a file integrity monitoring tool like CimTrak can help you manage your database security. Features like dynamic version control, unexpected change prevention, and real-time automated detection can help you monitor your database activity reliably and efficiently.
CimTrak can help you protect critical IT assets and achieve continuous, full-system protection. Explore an instant preview of CimTrak today to see how our solution can mitigate your risk in real-time.
Tags:
Cybersecurity
December 5, 2024